By understanding tooth infections and knowing when to seek help, you can protect your smile and your overall well-being.
They are a common yet potentially serious dental issue — while they may start as a localized problem, tooth infections have the potential to escalate quickly, causing not only severe discomfort but also posing risks to your health.
When it comes to dental health, knowledge and prompt action are your best allies in preventing minor issues from becoming major problems. This article will explore the signs and symptoms of tooth infections, including the causes and risk factors, potential complications, and available treatment options.
If you notice any combination of these signs, reach out to My Emergency Dental as soon as possible to receive prompt and effective care.

Understanding Tooth Infections
Tooth infections are a serious dental condition that can cause significant pain and potentially lead to more severe health issues if left untreated. At the heart of most tooth infections is what’s known as a dental abscess or tooth abscess – these terms are often used interchangeably.
A dental abscess, also called a tooth abscess, is essentially a pocket of pus that forms within the tissues surrounding a tooth. This occurs as a result of a bacterial infection which typically starts when bacteria invade the inner pulp of the tooth, usually through a cavity, chip, or crack in the tooth’s enamel.
Once bacteria enter the tooth, they multiply rapidly, feeding on the pulp tissue and causing inflammation. As the infection progresses, white blood cells rush to the area to fight off the bacteria. The battle between the bacteria and your immune system’s white blood cells, along with the breakdown of tissue, results in the formation of pus.
In short, a dental abscess is your body’s way of trying to contain the tooth infection and prevent it from spreading further. However, as the abscess grows, it puts pressure on the surrounding tissues, which is often the source of the intense pain associated with tooth infections.
There are different types of dental abscesses, depending on where they form. A periapical abscess forms at the tip of the tooth’s root, while a periodontal abscess forms in the gum tissue next to a tooth root. Both are serious conditions that require prompt dental attention.
If left untreated, the infection can spread beyond the initial abscess, potentially affecting other parts of the mouth, face, or even other areas of the body in severe cases. This is why it’s crucial to recognize the signs of a tooth infection early and seek appropriate dental care.
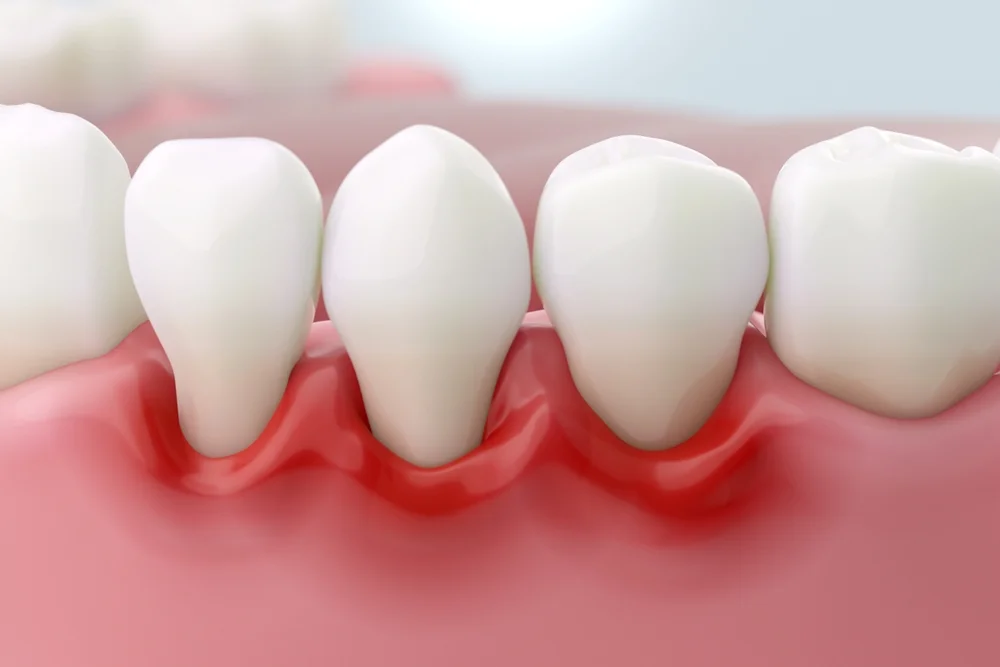
10 Common Signs and Symptoms of Tooth Infection
This section covers the 10 most common signs of tooth infection. If left untreated, tooth infections can spread beyond the initial abscess and affect other parts of the mouth, face, or even areas of the body in severe cases. As a result, it’s crucial to recognize the signs of a tooth infection early and seek appropriate dental care.
Please note that these symptoms can vary in severity, and you may not experience all of them. If you notice any combination of these signs, especially persistent pain or swelling, it’s crucial to seek dental care promptly. Early treatment can prevent the infection from spreading and potentially save the affected tooth.
Here are the 10 most common signs of tooth infection.
1. Pain and sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli
One of the most noticeable signs of a tooth infection is persistent, throbbing pain in the affected tooth or surrounding area. This pain often intensifies when you consume hot or cold foods and beverages. The sensitivity occurs because the infection irritates the nerve endings in and around the tooth.
2. Swelling and tenderness in the affected area
As the infection progresses, you may notice swelling in your cheek, jaw, or gums near the problem tooth. This area will likely feel tender to the touch. The swelling is caused by the body’s inflammatory response to the infection.
3. Persistent bad breath and unpleasant taste
The bacteria causing the infection can lead to a foul odor in your mouth that doesn’t go away with brushing or mouthwash. You might also experience a persistent bitter or unpleasant taste due to the pus from the abscess.
4. Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
In some cases, particularly when the infection has spread, you may find it hard to open your mouth fully or experience pain when trying to swallow. This can be due to swelling and inflammation affecting the surrounding muscles and tissues.
5. Fever and general feeling of illness
As your body fights the infection, you might develop a fever. This is often accompanied by fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell, similar to when you have the flu.
6. Pus discharge
You might notice pus oozing from the affected tooth or surrounding gum area. This is a clear sign of an abscess and indicates that the infection has progressed significantly.
7. Swollen lymph nodes
The lymph nodes in your neck or under your jaw may become swollen and tender. This is your body’s response to fighting the infection.
8. Facial swelling
In severe cases, the infection can cause noticeable swelling in your face or cheek on the side of the affected tooth.
9. Tooth discoloration
The infected tooth may become darker than the surrounding teeth due to the death of the pulp inside the tooth.
10. Loose tooth
As the infection damages the supporting structures around the tooth, including the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone, the affected tooth may become loose.
Understanding the Causes of Tooth Infection
Tooth infections are primarily caused by the invasion of bacteria into the tooth structure or surrounding tissues. While several factors can contribute to this bacterial invasion, tooth decay is the most common and significant cause.
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the tooth enamel. As the decay progresses, it can create small holes or cavities in the tooth. If left untreated, these cavities can deepen, allowing bacteria to penetrate into the inner layers of the tooth, including the pulp. Once bacteria reach the pulp, they can multiply rapidly, leading to infection and potentially an abscess.
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is another significant risk factor for tooth infections. This condition begins with the buildup of plaque and tartar along the gum line, which harbors bacteria. As gum disease advances, it can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive. These pockets can become infected, potentially leading to abscesses in the surrounding tissues. Moreover, severe gum disease can damage the supporting structures of the teeth, making them more vulnerable to infection.
Dental trauma can also play a crucial role in the development of tooth infections. When a tooth is chipped, cracked, or fractured due to an impact or accident, it creates an opening for bacteria to enter the tooth. Even if the damage isn’t immediately visible, micro-fractures can provide enough space for bacterial invasion. Similarly, injuries to the gums can create entry points for bacteria, potentially leading to infections in the surrounding tissues.
When to Seek Emergency Care
While tooth infections often begin as localized issues, they can potentially lead to severe complications if left untreated. Understanding these complications and knowing when to seek emergency care is crucial for preventing serious health risks.
A tooth infection, if not addressed promptly, can spread beyond the initial site. The infection can progress from the tooth to the surrounding tissues, including the jawbone, sinuses, and even the brain in very extreme cases. This spread occurs because the bacteria causing the infection can travel through the bloodstream or along tissue planes.
Recognizing the signs that indicate the need for emergency care is vital. You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe, uncontrollable pain that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Significant swelling of the face, jaw, or neck that may be affecting your ability to breathe or swallow.
- High fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) accompanied by chills, indicating that the infection may have spread.
- Rapid heart rate or difficulty breathing.
- Confusion or disorientation, which could suggest the infection is affecting your nervous system.
- Persistent vomiting or inability to keep fluids down.
In these situations, it’s crucial to go to an emergency room rather than waiting for a regular dental appointment. Emergency dental professionals can provide immediate treatment to prevent the infection from spreading further and manage any systemic effects.
In severe cases, particularly when there’s significant swelling or suspicion that the infection has spread beyond the oral cavity, a CT (Computed Tomography) scan may be necessary. A CT scan provides detailed, cross-sectional images of the affected areas, allowing healthcare providers to assess the extent of the infection and determine if the infection has spread to nearby structures like the sinuses or the eye socket.
It’s important to note that while emergency rooms can manage the acute symptoms and spread of a dental infection, definitive treatment will still require follow-up. The underlying dental issue that led to the infection will need to be addressed to prevent recurrence.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for tooth infections are focused on eliminating the infection, alleviating pain, and preserving the affected tooth if possible. The appropriate treatment depends on the severity of the infection and how far it has spread.
Root canal treatment is one of the most common and effective solutions for treating a tooth infection, especially when the infection has reached the pulp of the tooth. During this procedure, a dentist or endodontist removes the infected pulp from inside the tooth, carefully cleans and shapes the root canals, then fills and seals them. This process eliminates the source of the infection while preserving the natural tooth structure. After a root canal, a temporary crown is often placed on the tooth to protect it and restore its function. Root canal treatment has a high success rate and can save teeth that would otherwise need to be extracted.
While professional dental treatment is crucial for resolving a tooth infection, over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from pain and discomfort. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Acetaminophen is another option for pain relief, especially for those who can’t take NSAIDs. However, it’s important to remember that these medications only address the symptoms and do not treat the underlying infection. They should be used as a temporary measure while awaiting professional dental care.
Prevention and Oral Health Maintenance
Regular dental check-ups and deep dental cleanings form the cornerstone of preventive dental care. These routine visits, typically recommended every six months, serve multiple important purposes. During check-ups, dentists can detect early signs of decay, gum disease, or other oral health issues before they develop into more serious problems. Early detection often means simpler, less invasive, and less costly treatments. Professional cleanings, performed during these visits, remove plaque and tartar buildup that regular brushing and flossing might miss. This helps prevent the development of cavities and gum disease, which are primary precursors to tooth infections.
Proper oral hygiene practices at home are equally crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing infections. This includes brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and along the gum line, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacteria in the mouth. These habits help keep bacteria levels in check, strengthen tooth enamel, and maintain healthy gums – all of which contribute to preventing tooth infections.
Early intervention for dental issues is vital in preventing minor problems from escalating into serious infections. This means addressing tooth decay, gum inflammation, or dental injuries as soon as possible. For instance, having a small cavity filled immediately after it has been detected can prevent the decay from progressing deeper into the tooth, potentially avoiding the need for more extensive treatments like root canals or extractions. Similarly, treating early stages of gum disease can prevent it from advancing to more severe forms that can lead to tooth loss and increase the risk of infections.

A Final Word from My Emergency Dental
The importance of prompt action in the face of tooth infection cannot be overstated. Tooth infections don’t resolve on their own and can quickly escalate from a localized problem to a serious health risk.
By seeking treatment at the first sign of trouble, you can prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of your mouth or body. Early intervention not only limits the extent of the damage but often results in simpler, less invasive treatments. It can mean the difference between saving or losing a tooth, or in severe cases, avoiding life-threatening complications.
Don’t let fear or busy schedules deter you from seeking dental care. My Emergency Dental offers same-day appointments for urgent dental care, so we can accommodate hectic lifestyles and a variety of patient schedules. Don’t hesitate to reach out if you feel you may be suffering from tooth infection.